COPD
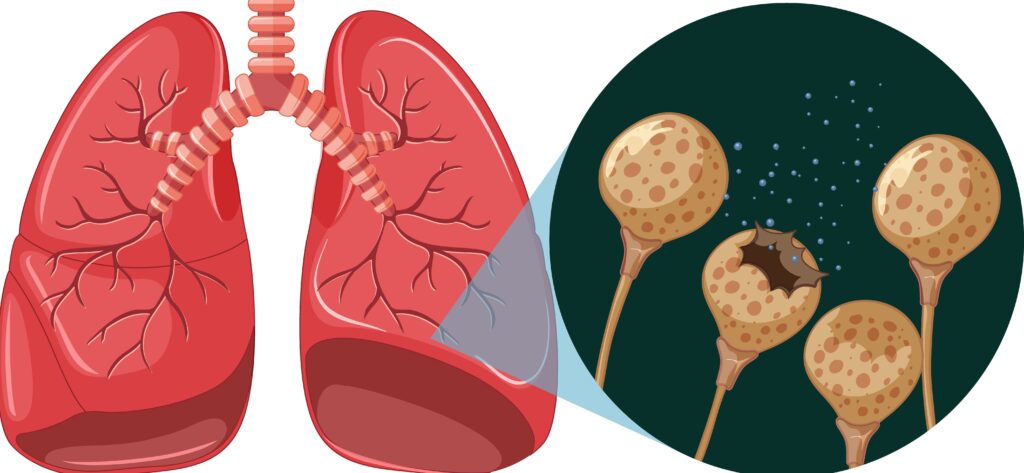
Overview of COPD
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a progressive lung disease characterized by persistent respiratory symptoms and airflow limitation. It primarily includes emphysema and chronic bronchitis.
Causes and Risk Factors
COPD is mainly caused by long-term exposure to irritating gases or particulate matter. Key risk factors include:
- Smoking: The leading cause of COPD.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to air pollution, chemical fumes, and dust.
- Genetic Factors: A rare genetic disorder called alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency can cause COPD.
- Occupational Hazards: Long-term exposure to workplace dust, vapors, and fumes.
Symptoms
COPD symptoms often develop slowly and worsen over time. Common symptoms include:
- Chronic Cough: Persistent cough that produces mucus.
- Shortness of Breath: Especially during physical activities.
- Wheezing: A whistling sound when breathing.
- Chest Tightness: Discomfort or pressure in the chest.
- Frequent Respiratory Infections: Increased susceptibility to colds, flu, and other respiratory illnesses.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing COPD involves several steps:
- Medical History and Physical Exam: Assessment of symptoms and risk factors.
- Spirometry: A lung function test that measures the amount of air a person can exhale and the speed of exhalation.
- Chest X-Ray or CT Scan: Imaging tests to visualize the lungs and identify signs of COPD.
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis: Measures the levels of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood.
Treatment and Management
While COPD is not curable, its symptoms can be managed through various treatments:
- Medications: Bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, and phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors to reduce symptoms and prevent complications.
- Oxygen Therapy: Supplemental oxygen for patients with severe COPD and low blood oxygen levels.
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation: A comprehensive program that includes exercise training, nutritional advice, and education to improve quality of life.
- Lifestyle Changes: Smoking cessation, avoiding lung irritants, and maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine.
Complications
COPD can lead to serious health complications, including:
- Respiratory Infections: Increased risk of pneumonia and other infections.
- Heart Problems: Higher risk of heart disease, heart attack, and stroke.
- Lung Cancer: Increased risk among COPD patients, especially smokers.
- Depression and Anxiety: Due to chronic illness and difficulty breathing.