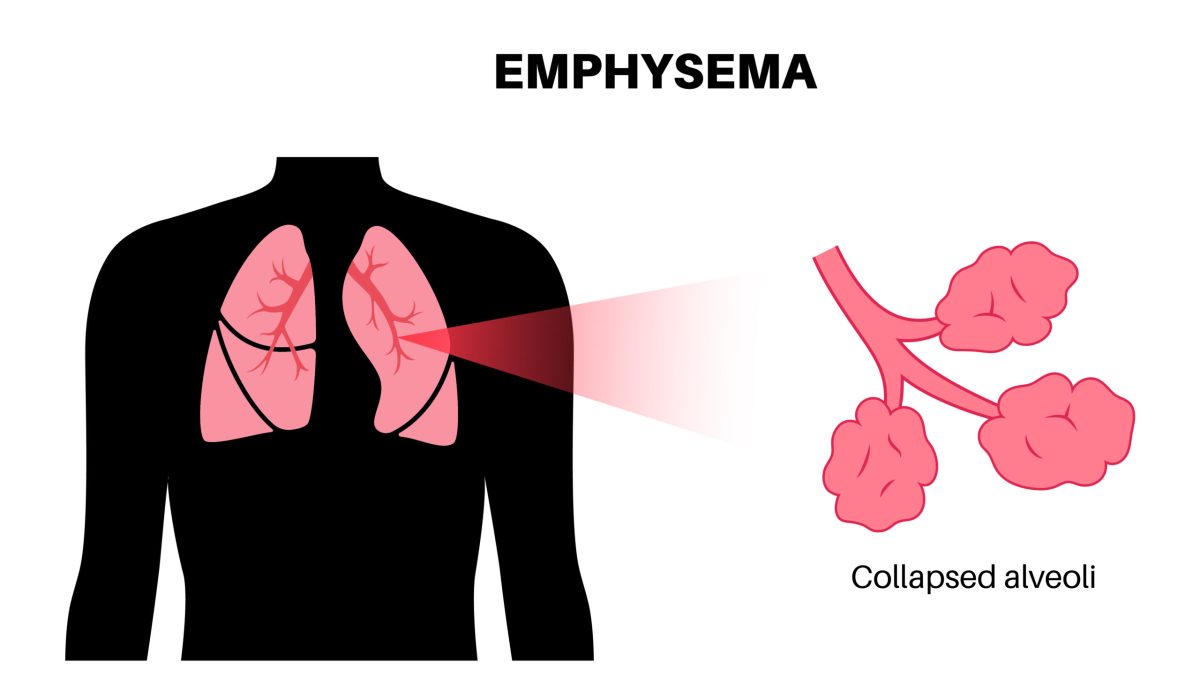
What Is Emphysema?
Emphysema is a type of chronic lung disease that affects your breathing. In this condition, the air sacs in your lungs become damaged. As a result, it becomes harder for your body to get the oxygen it needs. Many people with emphysema notice shortness of breath and a cough that does not go away. Because emphysema is a long-term problem, it is important to understand its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Early care can help you breathe easier and improve your quality of life.
Causes of Emphysema
There are several reasons why someone might develop emphysema. However, the most common cause is smoking. When you breathe in cigarette smoke, it damages the tiny air sacs in your lungs. Over time, this damage adds up and leads to emphysema. But smoking is not the only cause. Other causes include:
Even if you do not smoke, you can still get emphysema if you are exposed to these risks. Therefore, protecting your lungs is very important.
Symptoms of Emphysema
Emphysema symptoms often start slowly. At first, you may not notice any problems. But as the disease gets worse, you may experience:
Sometimes, people lose weight without trying. If you notice these signs, it is a good idea to talk to your doctor. Early treatment can help manage emphysema symptoms and slow the disease.
How Emphysema Is Diagnosed
Doctors use several tests to diagnose emphysema. First, they will ask about your symptoms and medical history. Next, they may listen to your lungs with a stethoscope. To confirm the diagnosis, your doctor may order:
Because emphysema can look like other lung problems, these tests help your doctor find the right answer. Early diagnosis is key to better pulmonary health.
Treatment Options for Emphysema
While there is no cure for emphysema, many treatments can help you feel better. Your doctor will suggest a plan based on your needs. Common treatment options include:
With the right treatment, many people with emphysema can stay active and enjoy life.
Lifestyle Tips and Prevention
There are steps you can take to protect your lungs and slow emphysema. For example, you can:
By making these changes, you can help prevent emphysema or keep it from getting worse. Even small steps can make a big difference in your pulmonary health.
Conclusion
Emphysema is a serious lung disease, but you can take steps to manage it. If you have symptoms or are at risk, talk to your doctor. Consult a pulmonologist for personalized advice on emphysema management. Early care and healthy habits can help you breathe easier and live better.