Tuberculosis
Overview of Tuberculosis
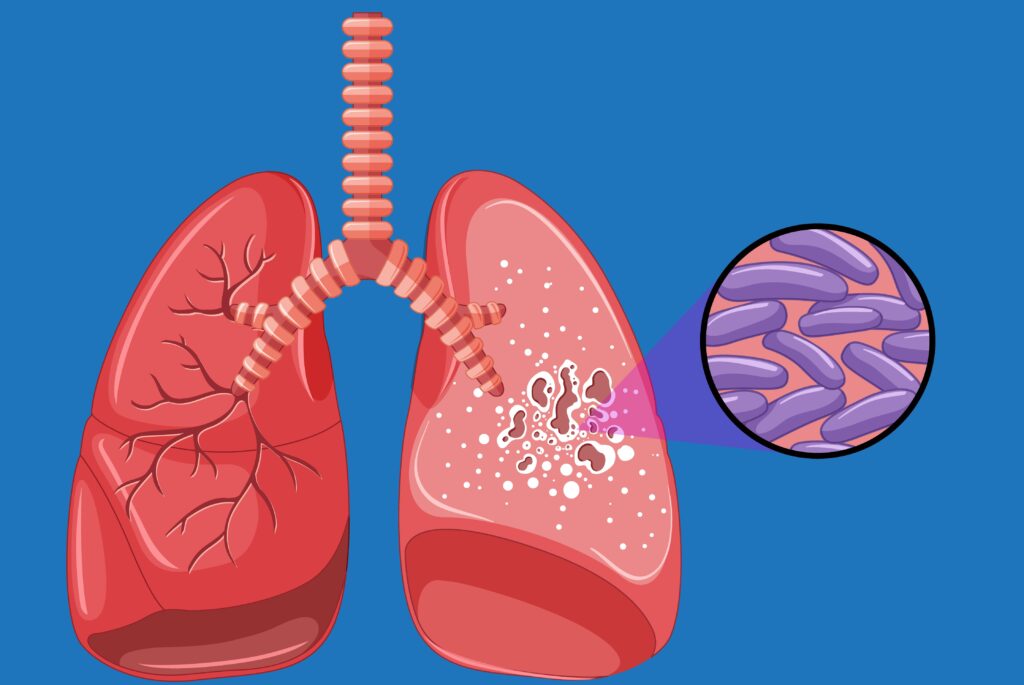
Tuberculosis (TB) is a contagious bacterial infection caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It primarily affects the lungs but can also impact other parts of the body, such as the kidneys, spine, and brain. TB is a significant public health issue, especially in developing countries.
Causes and Transmission
TB is transmitted through airborne particles when an infected person coughs, sneezes, talks, or laughs. The bacteria can be inhaled by individuals nearby, leading to infection. Not everyone infected with TB bacteria becomes sick; TB can be latent (inactive) or active.
Types of Tuberculosis
- Latent TB: The bacteria are present in the body but inactive. The person does not show symptoms and is not contagious. However, latent TB can turn into active TB if not treated.
- Active TB: The bacteria are active, causing symptoms and being contagious. Active TB requires immediate treatment to prevent spread and complications.
Symptoms
Symptoms of active TB include:
- Persistent Cough: Lasting more than three weeks, often with sputum and sometimes blood.
- Fever: Especially in the evening.
- Night Sweats: Excessive sweating during the night.
- Weight Loss: Unintentional weight loss and loss of appetite.
- Fatigue: General feeling of tiredness and weakness.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing TB involves several tests:
- Tuberculin Skin Test (TST): A small amount of tuberculin is injected under the skin, and the area is checked for a reaction after 48-72 hours.
- Blood Tests: Interferon-gamma release assays (IGRAs) to detect TB infection.
- Chest X-Ray: Identifies lung abnormalities suggestive of TB.
- Sputum Tests: Microscopic examination and culture of sputum to detect TB bacteria.
Treatment
TB treatment involves a combination of antibiotics taken over an extended period, usually six to nine months. Common medications include isoniazid, rifampin, ethambutol, and pyrazinamide. Completing the full course of treatment is crucial to prevent drug-resistant TB.
Prevention
Preventive measures include:
- Vaccination: Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine is administered in countries with high TB prevalence.
- Screening and Treatment: Identifying and treating latent TB to prevent progression to active TB.
- Infection Control: Measures such as using masks, ensuring good ventilation, and isolating infectious patients.